The latest findings from Shell’s LNG Outlook 2024 reveal a robust trajectory for liquefied natural gas LNG demand, projecting a remarkable surge of over 50% by 2040. The report underscores the accelerating momentum of industrial coal-to-gas transitioning in China and heightened LNG consumption in South Asian and Southeast Asian nations to fuel their burgeoning economies.
In 2023, global LNG trade escalated to 404 million tonnes, marking a notable uptick from 2022 figures. Despite the growth, tight supplies of LNG have curbed further expansion, while maintaining prices and volatility above historical averages. Notably, certain regions have already reached peak natural gas demand, yet global consumption continues to ascend, with anticipated LNG demand reaching a staggering 625-685 million tonnes annually by 2040, as per industry forecasts.
Steve Hill, Executive Vice President for Shell Energy, highlighted China’s pivotal role in driving LNG demand growth, citing the country’s strategic shift from coal to gas to mitigate carbon emissions. With China’s coal-heavy steel sector alone emitting more carbon than the combined totals of the UK, Germany, and Turkey, the transition to gas emerges as a critical strategy to combat carbon emissions and local air pollution.
Looking ahead, dwindling domestic gas production in parts of South Asia and Southeast Asia is poised to fuel a surge in LNG demand, primarily driven by the burgeoning need for fuel in gas-fired power plants and industrial sectors. However, meeting this escalating demand necessitates substantial investments in gas import infrastructure across these regions.
Furthermore, the report underscores gas’s complementary role alongside wind and solar power, particularly in regions with high renewables penetration. Gas provides both short-term flexibility and long-term supply security in such energy mixes.
In the realm of European energy security, LNG remains a linchpin, especially following a downturn in Russian pipeline exports in 2022. The integration of new regasification facilities has bolstered energy supply security in Europe, with LNG imports maintaining steady levels despite an overall decline in gas demand in 2023. Favorable factors such as mild winter temperatures, robust gas storage levels, increased nuclear power generation, and a modest economic rebound in China have collectively stabilized gas prices in key importing regions like Europe and East Asia. Nonetheless, prices and volatility persist at elevated levels compared to pre-2021 periods.
While the global gas market in 2023 was adequately supplied, the absence of Russian pipeline gas to Europe and limited LNG supply growth underscores the persisting structural tightness in the global gas market. This structural tightness signals continued challenges in ensuring stable and secure energy supplies in the coming years.
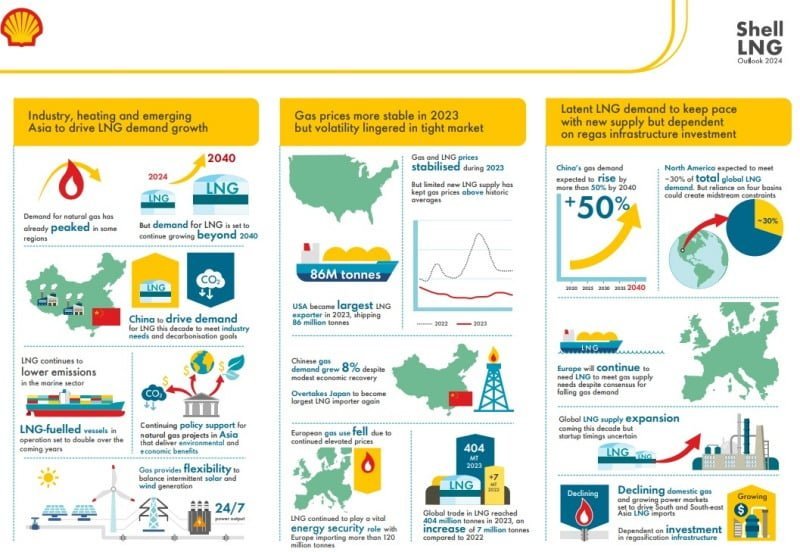
Key Findings from Shell LNG Outlook:
- Growing LNG Demand Drivers
- Industry needs and decarbonization goals, particularly in emerging Asian markets, are propelling LNG demand.
- LNG continues to gain traction in the marine sector, contributing to emission reduction efforts globally.
- China’s robust industrial growth and decarbonization initiatives are set to drive significant LNG demand in the coming decade.
- Policy Support and Environmental Benefits
- Continued policy support for natural gas projects in Asia underscores the environmental and economic benefits of LNG.
- Natural gas provides flexibility for balancing intermittent renewable energy sources like solar and wind power.
- Market Dynamics
- Gas prices showed increased stability in 2023, with the USA emerging as the largest LNG exporter.
- Limited new LNG supply has kept gas prices above historic averages in some regions.
- Regional Demand Trends
- Despite economic recovery challenges, China’s gas demand surged by 8%, making it the largest LNG importer again, surpassing Japan.
- European gas consumption declined due to elevated prices, though LNG remained crucial for ensuring energy security.
- Global LNG Trade
- Global LNG trade reached 404 million tonnes in 2023, marking a significant increase from the previous year.
- Latent LNG demand is expected to align with new supply, contingent upon investments in regasification infrastructure.
- Future Projections
- North America is anticipated to meet approximately 30% of global LNG demand, albeit with potential midstream constraints.
- Europe is expected to continue relying on LNG to meet gas supply needs, despite predictions of falling gas demand.
- Uncertainties persist regarding the startup timings of upcoming LNG supply expansions.
- Asia-Pacific Dynamics
- South and Southeast Asia are expected to witness increased LNG imports due to declining domestic gas reserves and growing power markets, contingent upon infrastructure investment.
Source Shell

