Singapore | January 13, 2026 – Singapore has reported a record-breaking year for port operations, bunkering activity and maritime industry growth in 2025, underpinned by resilient global trade flows and rising marine fuel demand. The performance was announced by Senior Minister of State for Law and Transport, Mr. Murali Pillai, at the Singapore Maritime Foundation (SMF) New Year Conversations event.
Table of Contents
Record Port Throughput and Marine Fuel Sales
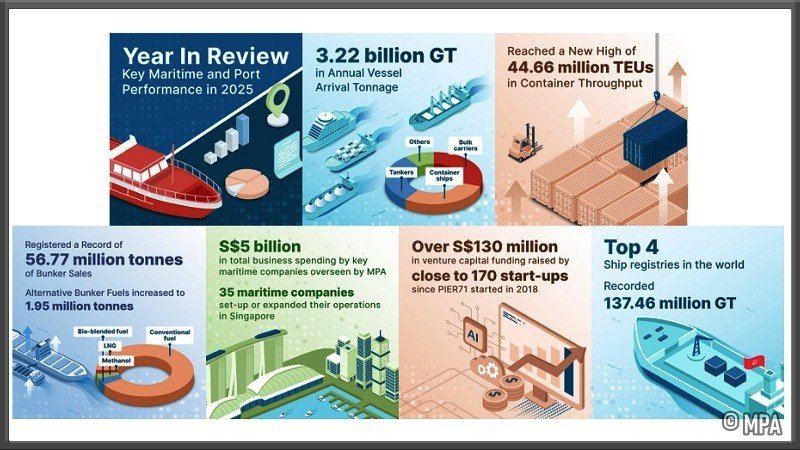
Singapore achieved historic highs across several key maritime indicators in 2025. Total vessel arrivals reached 3.22 billion gross tonnage (GT), marking a 3.5% increase year-on-year, while container throughput climbed to 44.66 million TEUs, an 8.6% rise from 2024.
Marine fuel sales also set a new benchmark, reaching 56.77 million tonnes, up 3.4% year-on-year, reinforcing Singapore’s position as the world’s largest bunkering hub. Notably, the uptake of alternative marine fuels continued to accelerate, rising to 1.95 million tonnes in 2025, compared with 1.35 million tonnes in 2024.
Reflecting its global standing, Singapore was named the world’s leading container port in DNV-Menon’s inaugural Leading Container Ports of the World report. The port was also recognised as Best Global Seaport for the fourth time and Best Seaport in Asia for the 37th time at the Asian Freight, Logistics and Supply Chain Awards 2025.
Strengthening Readiness for a Multi-Fuel Bunkering Future
As part of its strategy to remain future-ready, the Maritime and Port Authority of Singapore (MPA) announced a series of initiatives to support the transition to low- and zero-carbon fuels.
From 14 January 2026, MPA will open applications for new LNG bunker supply licences to meet growing industry demand. In tandem, MPA will introduce Standards for Port Limit LNG Bunker Vessels, covering vessel equipment, operational performance and efficiency, with a strong focus on safety.
MPA and Enterprise Singapore, through the Singapore Standards Council (SSC), will also upgrade the existing Technical Reference for LNG Bunkering (TR56) to a full Singapore Standard by Q2 2026, strengthening requirements for safe, transparent and quality-assured LNG bunkering operations.
In addition, Singapore will publish its first Technical Reference for Ammonia Bunkering in Q2 2026, providing guidance for safe and reliable ammonia bunkering and supporting early trials and adoption.
Green and Digital Shipping Corridors Expand
Singapore expanded its network of Green and Digital Shipping Corridors (GDSCs) in 2025, establishing new corridors with India and the Republic of Korea, while elevating the existing corridor with China to the national level. This brings the total number of GDSCs to nine.
The corridors aim to pilot solutions that improve supply chain resilience, operational efficiency and environmental sustainability. Planned projects for 2026 include:
- Development of common emissions-reporting frameworks
- Enhanced digital data exchange
- Alternative fuel trials along participating trade routes
These efforts complement the appointment of a Keppel-led consortium in October 2025 to conduct front-end engineering design (FEED) studies for ammonia power generation and bunkering, as well as the awarding of three methanol bunkering licences in November 2025.
Digital Bunkering Reaches Full Adoption
Singapore achieved 100% adoption of digital bunkering across all bunker suppliers by August 2025. The system enables the issuance and verification of electronic bunker delivery notes (e-BDNs) via an online enquiry facility.
The transition has significantly improved transparency and productivity across bunkering operations, reducing manual paperwork and saving an estimated 40,000 man-days annually in business process efforts.
Continued Growth as an International Maritime Centre
Singapore further reinforced its status as a leading International Maritime Centre (IMC) in 2025. During the year, 35 maritime companies opened or expanded operations in Singapore, bringing the total to over 200 international shipping groups.
Collectively, these companies contributed approximately S$5 billion in annual business spending to the economy. Singapore also retained its top ranking in the Xinhua-Baltic International Shipping Centre Development Index.
Maritime digitalisation and R&D collaboration continued to deepen, with multiple MoUs signed or renewed. New technology and innovation centres established in Singapore include:
- ABS Singapore Maritime Safety Centre
- BV–Singapore Institute of Technology Centre for Maritime Electrification
- RINA Technology Demonstration Centre
Singapore Registry of Ships Hits Record Tonnage
The Singapore Registry of Ships (SRS) closed 2025 with a record 137.46 million GT, representing an increase of approximately 27% from 2024, making it the fourth-largest ship registry globally.
In 2025, SRS awarded 34 Green Ship Certificates and has flagged five methanol-fuelled vessels since 2020. The registry expects to flag its first ammonia dual-fuelled vessel within the next two years, highlighting growing confidence in alternative fuel technologies.
Shaping Global Maritime Standards
Singapore continued to play an active role in shaping international maritime governance. In 2025, the country was re-elected to the Council of the International Maritime Organization (IMO) for the 17th time and was elected to the International Organization for Marine Aids to Navigation (IALA) Council for the 2025–2027 term.
Building the Maritime Workforce of the Future
MPA, in partnership with government agencies, industry stakeholders, unions and educational institutions, continued efforts to strengthen maritime talent development. Initiatives include:
- Internship and scholarship programmes
- Enhanced Tripartite Maritime Training Award for mid-career entrants
- Expansion of the Maritime Leadership Programme into adjacent sectors such as trading and logistics
In collaboration with the National University of Singapore (NUS), the MPA-SMF Joint Office on Talent and Skills successfully rolled out stackable micro-credentials in data science and analytics. The inaugural Foundation Course in Data Analytics attracted 58 participants from 40 companies in September 2025, with a second public run scheduled for January 2026. New courses in AI competencies and sustainability are also under development.
Outlook for 2026
Looking ahead, the global economy enters 2026 amid rising geopolitical tensions and trade uncertainties. Despite these challenges, global seaborne trade is expected to remain resilient, particularly in commodity trades where diversification and route re-alignment continue to drive shipping demand.
Singapore reaffirmed its commitment to working closely with the global maritime and bunkering community to navigate uncertainties, support the energy transition, and seize emerging opportunities in the years ahead.
About the Maritime and Port Authority of Singapore (MPA)
Established in 1996, the Maritime and Port Authority of Singapore (MPA) develops Singapore as a global hub port and international maritime centre while safeguarding the nation’s strategic maritime interests. MPA serves as the maritime regulator, port planner, and international maritime representative, driving Singapore’s digitalisation and decarbonisation agenda. Working closely with industry, academia, and other government agencies, MPA enhances safety, security, environmental protection, and manpower development to sustain Singapore’s maritime growth.
Source: MPA Singapore